How to Create a Sleep HRV Tracker Using Flask, ChartJS, and Terra API
This article will teach you how to use the Terra API to create a simple Sleep HRV Tracker. We will use Python and Flask to consume data from the Terra Webhook, store it in a database, and then show it using a ChartJS graph.
Here is an image of the web application we are going to build:
Step 1 - Obtain Your Credentials from The Terra Dashboard
To communicate with a wearable through the Terra API, you need the following:
- Your API Key
- Your Dev ID
Go to your Terra Dashboard; under Connections, you will find your API Key and Dev ID in the bottom right corner in the API Credentials Popup. They are used in virtually every interaction with the API - keep them safe!
Step 2 - Create a Flask Webhook Consumer and Serve it with Ngrok
Create a virtual environment and activate it:
python -m venv env
source env/bin/activate
Install the necessary packages:
pip install Flask Flask-SQLAlchemy terra-python
The terra-python package is a wrapper for the Terra endpoints and models. We'll use it to verify and authenticate incoming webhook data.
Next, create a small Flask app file called app.py:
import logging
from flask import Flask, Response, request, render_template
from terra.base_client import Terra
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
_LOGGER = logging.getLogger("app")
terra = Terra(api_key='<API-KEY>',
dev_id='<DEV-ID>',
secret='<SIGNING-SECRET>')
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/", methods=["GET", "POST"])
def consume_terra_webhook() -> Response:
if request.method == 'POST':
# Get data from the Terra Webhook
body = request.get_json()
# Log that the Webhook was recieved
_LOGGER.info(
"Received webhook for user %s of type %s",
body.get("user", {}).get("user_id"),
body["type"])
# Just a health check, return 200
if body["type"] == 'healthcheck':
return Response(status=200)
# Verify Terra Signature
verified = terra.check_terra_signature(request.get_data().decode("utf-8"),
request.headers['terra-signature'])
# The data is verified
if verified:
return Response(status=200)
else:
return Response(status=403)
# Handle GET requests
if request.method == 'GET':
return '<h1>Sleep HRV Tracker</h1>'
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host="localhost", port=8080)
Make sure to fill in <API-KEY> and <DEV-ID> with your API key and developer ID. The signing secret will be added later in this article.
This simple Flask web application serves as a webhook endpoint for Terra.
The code performs the following:
- Initializes logging with INFO level.
- Initializes a Terra client with the provided API key, and developer ID.
- Creates a Flask web application instance
app. - Defines a route ("/") that handles both GET and POST requests.
In the consume_terra_webhook() function, you have two conditions, one for handling POST requests and one for GET requests.
If the request is a POST request, this means that the Terra API has sent some data through a Webhook. So, the code does the following:
- Retrieves JSON data from the request body.
- Logs information about the received webhook, including user ID and data type.
- If the webhook type is a "healthcheck" respond with a 200 status.
- Verifies the Terra signature by comparing it with the calculated signature using the
check_terra_signature()method. This will not work for now, as we haven't yet added a signing secret. - In the
if verified:condition, the signature is verified, so we respond with a 200 status for now; you will later modify this part of the code, so that it inserts data into a database. We will also respond with an HTTP 201 status code instead of 200 to signify that a resource was added to the server. - If the signature is not verified, respond with a HTTP 403 FORBIDDEN status.
On the other hand, if the request is a GET request, the code returns a simple H1 header. We will later modify this to display a ChartJS graph for HRV data.
Run the application on port 8080:
flask --app app run -p 8080
As Terra cannot send Webhook data to your local development server, you have to expose your server to the Internet using Ngrok. To install it, check out this page.
Once you install Ngrok, create an account, then obtain your authentication token from the Ngrok dashboard. Once you get your authtoken, add it to your Ngrok agent using the following command:
ngrok config add-authtoken <TOKEN>
This will allow you to access some features such as rendering HTML files.
Once you set up Ngrok, use it to expose your Flask application that is currently running on port 8080:
ngrok http 8080
This command will give you a URL under Forwarding. Copy this URL. This is your Server URL, and you will use it to connect to a Terra Webhook in the next step.
Step 3 - Connect a Terra Webhook with Your Server
You will now connect a test wearable with your Flask app.
Note: We will use FitBit in this demo.
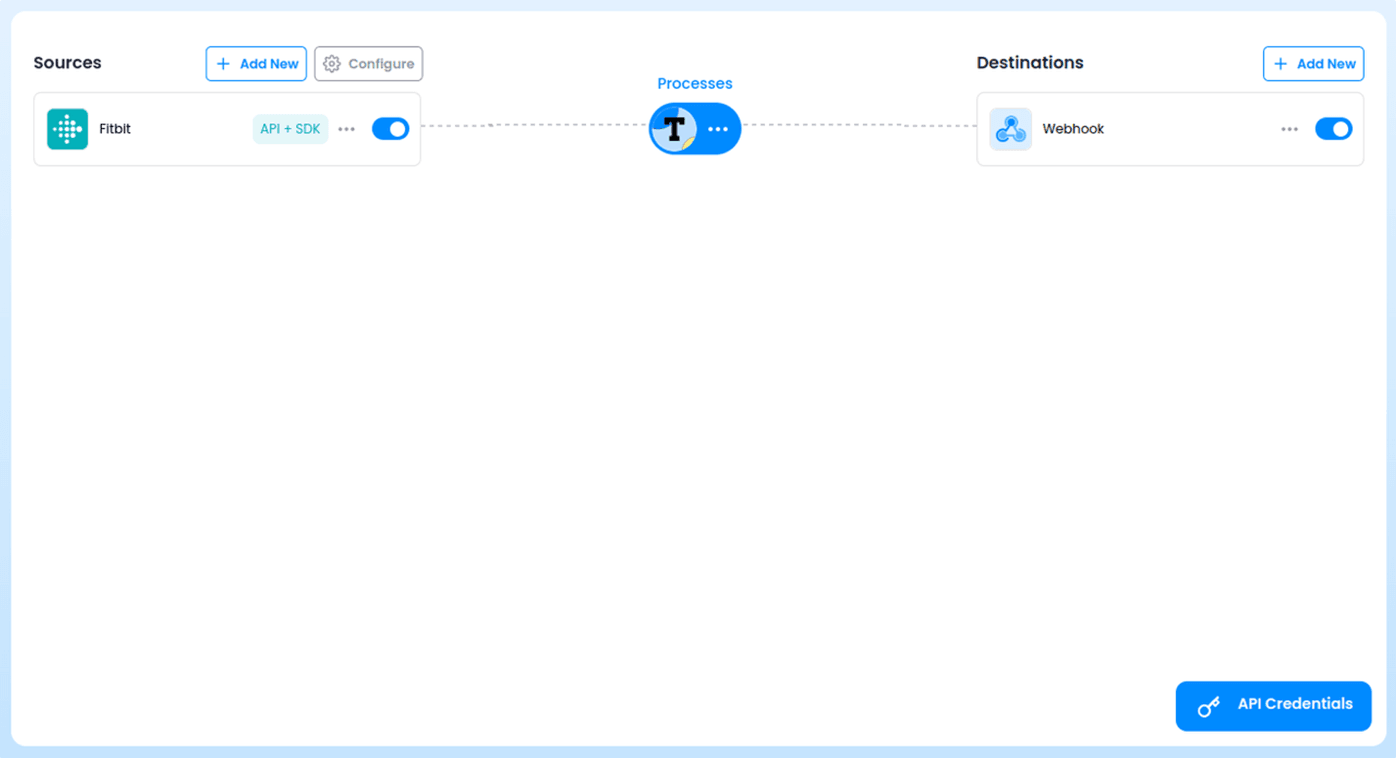
Go to your Terra Dashboard, then in Connections. Under Sources, click Add Sources, and select Fitbit, then Save.
Next, under Destinations click Add Destination, then select Webhook, then Next.
Put your Ngrok Server URL under host.
The Connections dashboard should now look like so:
Now, you need to obtain your Signing secret. Click the three dots to the right of Webhook then Edit.
Copy the Signing secret. This is needed to authenticate and verify Webhook requests.
To use your Webhook's signing secret, modify the secret parameter in your Terra initiation inside your app.py Flask application:
terra = Terra(api_key='<API-KEY>',
dev_id='<DEV-ID>',
secret='<PASTE-SIGNING-SECRET-HERE>')
Once modified, remember to rerun your Flask app:
flask --app app run -p 8080
Note: Make sure Ngrok is still running. If you've stopped it and restarted it, your Server URL will change, so make sure to edit the Webhook host in your Terra Dashboard and replace the old Ngrok URL with the new one.
We will now test the Webhook connection. In the Terra Dashboard, go to Tools > Generate > Select Data Source > Fitbit.
Then click on Sleep, then click Generate test data.
Once data is generated. Click Send to Webhook.
Go back to your Flask server and wait for a few seconds. You should see the following message in the logs:
INFO:app:Received webhook for user <Your User ID> of type sleep
INFO:werkzeug:127.0.0.1 - - [06/Dec/2023 21:08:07] "POST / HTTP/1.1" 200 -
This means you have successfully connected a Terra Webhook with your Flask application and you are receiving data! Next, you'll modify app.py to store the data inside an SQLite database.
Step 4 - Storing Sleep HRV data in an SQLite Database
Now that you are receiving wearable data from the Terra Webhook, you can use Flask-SQLAlchemy to store this data in an SQL database. We will use an SQLite database in this demonstration.
Open your app.py file and modify it by importing and setting up Flask-SQLAlchemy, then adding a new HRV_Sampledatabase model, so that everything above the @app.route("/", methods=["GET", "POST"]) line looks as follows:
# app.py
import logging
from flask import Flask, Response, request, render_template
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
from terra.base_client import Terra
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
_LOGGER = logging.getLogger("app")
terra = Terra(api_key='<API-KEY>',
dev_id='<DEV-ID>',
secret='<SIGNING-SECRET>')
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:///app.db'
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
# Database Table for Sleep HRV Samples
class HRV_Sample(db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'hrv_sample'
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
timestamp = db.Column(db.String)
hrv_rmssd = db.Column(db.Integer)
Save and close the file.
Here, you set up a database URI that will point to an SQLite database called app.db. This database file will be created inside a new instance folder that will be automatically added to your Flask project folder.
You also add a Flask-SQLAlchemy database model that represents a table called HRV_Sample with a column for an ID, a timestamp, and an HRV RMSSD value, these last two items are provided to us by the Terra Sleep API.
Next, inside your Flask application folder, with your environment activated, open the Flask Shell to create the database file and HRV Sample table:
flask shell
>>> from app import db, HRV_Sample
>>> db.create_all()
>>> exit()
You should see a new app.db file inside an instance folder in your Flask project folder.
Next, modify the if verified condition code in your app.py, where you handle POST requests, from this:
# ...
# The data is verified
if verified:
return Response(status=200)
To this:
# ....
# The data is verified
if verified:
# Extract HRV Samples
hrv_samples = body['data'][0]['heart_rate_data']['detailed']['hrv_samples_rmssd']
# Add timestamps & HRV values to a DB
_LOGGER.info("Adding timestamps and HRV to the Database")
for sample in hrv_samples:
db_hrv_sample = HRV_Sample(timestamp=sample['timestamp'],
hrv_rmssd=sample['hrv_rmssd'])
db.session.add(db_hrv_sample)
# Apply changes to the database
db.session.commit()
return Response(status=201)
# ....
Save and close the file.
Here, you extract the HRV samples from the body variable, which holds the Sleep data sent by the Terra API. You Log the database insertion, then loop through the provided samples and insert each timestamp and its corresponding HRV RMSSD value into the database session.
Finally, you call db.session.commit() to apply changes to the database, then respond with an HTTP 201 status code.
The full file should now be like this:
# app.py
import logging
from flask import Flask, Response, request, render_template
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
from terra.base_client import Terra
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
_LOGGER = logging.getLogger("app")
terra = Terra(api_key='<API-KEY>',
dev_id='<DEV-ID>',
secret='<SIGNING-SECRET>')
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:///app.db'
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
# Database Table for Sleep HRV Samples
class HRV_Sample(db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'hrv_sample'
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
timestamp = db.Column(db.String)
hrv_rmssd = db.Column(db.Integer)
@app.route("/", methods=["GET", "POST"])
def consume_terra_webhook() -> Response:
if request.method == 'POST':
# Get data from the Terra Webhook
body = request.get_json()
# Log that the Webhook was recieved
_LOGGER.info(
"Received webhook for user %s of type %s",
body.get("user", {}).get("user_id"),
body["type"])
# Just a health check, return 200
if body["type"] == 'healthcheck':
return Response(status=200)
# Verify Terra Signature
verified = terra.check_terra_signature(request.get_data().decode("utf-8"),
request.headers['terra-signature'])
# The data is verified
if verified:
# Extract HRV Samples
hrv_samples = body['data'][0]['heart_rate_data']['detailed']['hrv_samples_rmssd']
# Add timestamps & HRV values to a DB
_LOGGER.info("Adding timestamps and HRV to the Database")
for sample in hrv_samples:
db_hrv_sample = HRV_Sample(timestamp=sample['timestamp'],
hrv_rmssd=sample['hrv_rmssd'])
db.session.add(db_hrv_sample)
# Apply changes to the database
db.session.commit()
return Response(status=201)
else:
return Response(status=403)
# Handle GET requests
if request.method == 'GET':
return '<h1>Sleep HRV Tracker</h1>'
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host="localhost", port=8080)
To test that this new added code works, go back to the Terra Dashboard, generate new data, then click Send to Webhook.
You should see the following two lines in your Flask server logs:
INFO:app:Adding timestamps and HRV to the Database
INFO:werkzeug:127.0.0.1 - - [06/Dec/2023 21:34:36] "POST / HTTP/1.1" 201 -
With the wearable data now stored inside our database, we can modify our Flask application and use ChartJS to create a simple sleep HRV tracker app.
Step 5 - Creating the Sleep HRV Tracker with ChartJS
To create the sleep HRV tracker, we will modify the part of code that handles GET requests.
Open app.py, then add a datetime import and a new date_time_format() function above the @app.route("/", methods=["GET", "POST"]) line.
import logging
from datetime import datetime
from flask import Flask, Response, request, render_template
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
from terra.base_client import Terra
# ...
# ...
# ...
# Function to format timestamps to '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'
# (Makes the ChartJS graph easier to read)
def date_time_format(timestamp):
return datetime.fromisoformat(timestamp[:-6]).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
@app.route("/", methods=["GET", "POST"])
# ...
Note: The rest of the code is omitted and referenced as # .... The date_time_format() function will be used to make timestamps easier to read.
Next, modify the GET request handler from this:
# Handle GET requests
if request.method == 'GET':
return '<h1>Sleep HRV Tracker</h1>'
To this:
# Handle GET requests
if request.method == 'GET':
latest_hrv_samples = HRV_Sample.query.order_by(
HRV_Sample.timestamp.desc()) \\\\
.limit(10).all()[::-1]
# Extract timestamps & make them readable
timestamps = [date_time_format(s.timestamp) for s in latest_hrv_samples]
# Extract HRV values
hrv_values = [s.hrv_rmssd for s in latest_hrv_samples]
return render_template('graph.html',
timestamps=timestamps,
hrv_values=hrv_values)
Save and close the file.
Here, you get the latest 10 HRV samples from the database, extract timestamps and HRV values, then render a template file called graph.html passing it the extracted timestamps and HRV values.
Next, create a templates folder inside your Flask project folder and add a graph.html file to it with the following content:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Sleep HRV Tracker</title>
<!-- Add Chart.js CDN -->
<script src="<https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/chart.js>"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:50%; margin:auto;">
<h1>Simple Terra Sleep HRV Tracker</h1>
<canvas id="barChart"></canvas>
</div>
<script>
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function () {
var ctx = document.getElementById('barChart').getContext('2d');
var myChart = new Chart(ctx, {
type: 'line',
data: {
labels: {{ timestamps | tojson | safe }},
datasets: [{
label: 'HRV RMSSD',
data: {{ hrv_values | tojson | safe }},
backgroundColor: 'rgba(75, 192, 192, 0.2)',
borderColor: 'rgba(75, 192, 192, 1)',
borderWidth: 1
}]
},
options: {
scales: {
y: {
beginAtZero: true
}
}
}
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
This ChartJS code generates a line chart with the provided timestamps and HRV RMSSD values.
To test the application, ensure your Flask server is running, and use your browser to access your Ngrok Server URL.
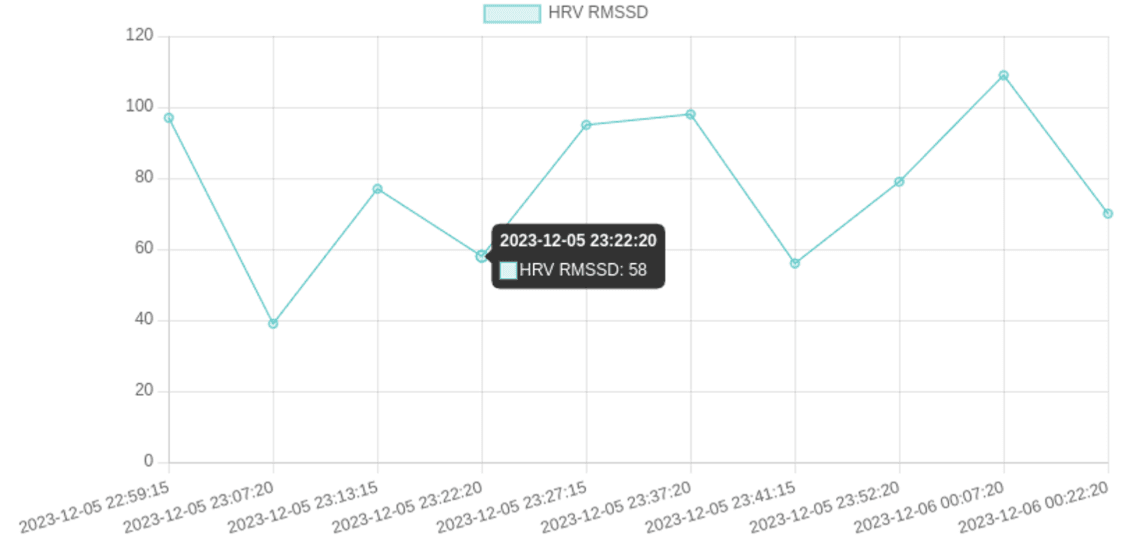
You should now see your Sleep HRV Tracker app:
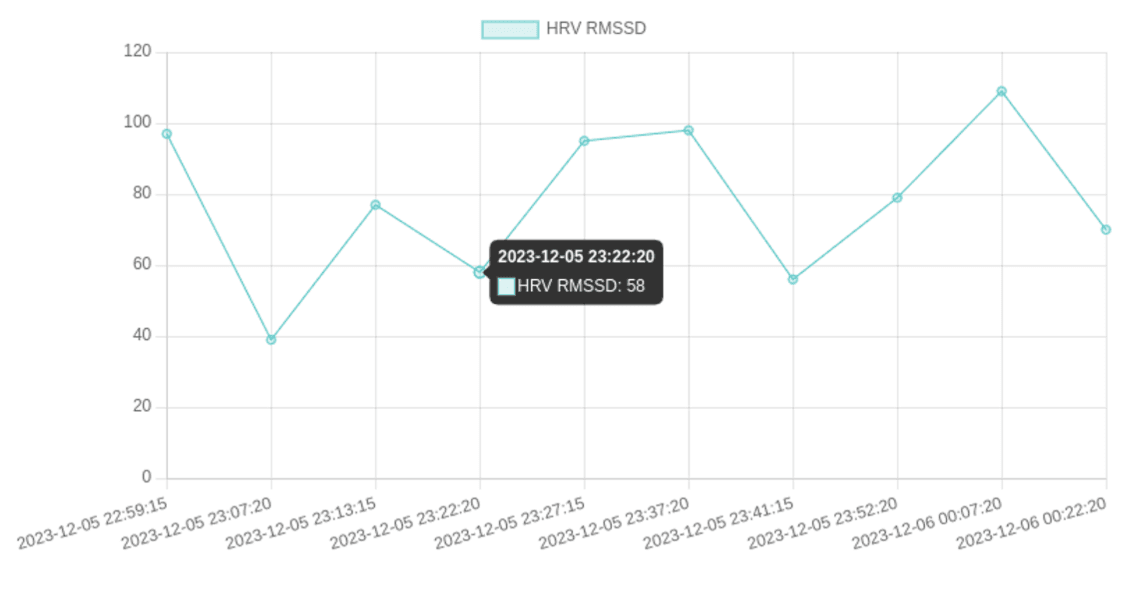
Conclusion
Congrats! You've learned how to use the Terra API to make a Sleep HRV Tracker. Check out the documentation to learn more about the awesome things you can build with Terra!





